問(wèn)題來(lái)源:
1. Introduction
|
Standard costing card - Product 123 |
$ |
|
Direct material (standard quantity × standard price) |
|
|
material X - 3kg at $4 per kg |
12 |
|
material Y - 9litres at $2 per litre |
18 |
|
Direct labour (standard time × standard rate) |
|
|
grade A - 6hrs at $1.5 per hr |
9 |
|
grade B - 8hrs at $2 per hr |
16 |
|
Standard direct cost |
55 |
|
Variable production overhead (14hrs × $0.5 per hr) |
7 |
|
Standard variable cost of production |
62 |
|
Fixed production overhead (14hrs × $4.5 per hr) |
63 |
|
Standard full production cost |
125 |
|
Administration and marketing overhead |
15 |
|
Standard cost of sales |
140 |
|
Standard profit |
20 |
|
Standard selling price |
160 |
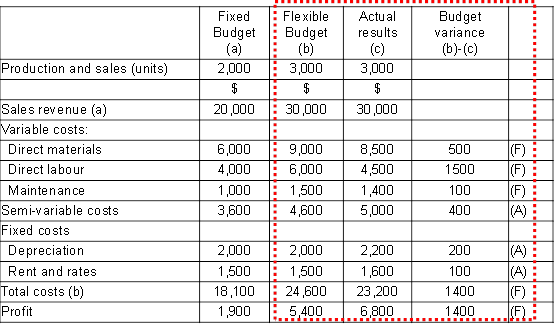
A standard cost is a predetermined estimated unit cost, used for inventory valuation and control. It is most suited to mass production and repetitive assembly work.
A variance is the difference between a standard cost and the actual cost incurred. The same comparisons may be made for revenues. The purpose by which the total difference between standard and actual results is analysed is known as variance analysis.
When actual results are better than expected results, we have a favourable variance (F). If actual results are worse than expected results, we have an adverse variance (A).
Types of performance standard:
|
Ideal (理想標(biāo)準(zhǔn)成本) |
? Based on perfect operating conditions: no wastage, no spoilage, no inefficiencies, no idle time, no breakdowns. ? Unfavourable motivational impact because reported variances will always be adverse. |
|
Attainable (正常標(biāo)準(zhǔn)成本) |
? Some allowance is made for wastage and inefficiencies. ? Provide a useful psychological incentive but challenging target of efficiency. |
|
Current (現(xiàn)行標(biāo)準(zhǔn)成本) |
? Based on current working conditions (current wastage, current inefficiencies). ? They do not attempt to improve on current levels of efficiency. |
|
Basic (基本標(biāo)準(zhǔn)成本) |
? Kept unaltered over a long time, and may be out of date. ? Used to show changes. ? Least useful and least common type of standard. |

李老師
2023-11-20 14:19:22 1365人瀏覽
D選項(xiàng)降價(jià)后的線的延長(zhǎng)線可以回到原點(diǎn),,A不能,。
追溯性打折的圖示:

相關(guān)答疑
-
2025-06-26
-
2025-06-14
-
2023-11-20
-
2023-11-20
-
2023-11-20
您可能感興趣的ACCA試題
- 單選題 某投資者一年前以每股40美元的價(jià)格購(gòu)得股票,,每年的股息為1.50美元。目前該股的價(jià)格為45美元,,持有該股票一年的收益率是多少( ),。
- 單選題 投資者已經(jīng)收集了以下四種股票的信息: 股票 β 平均收益(%) 回報(bào)的標(biāo)準(zhǔn)差(%) W 1.0 9.5 13.2 X 1.2 14.0 20.0 Y 0.9 8.4 14.5 Z 0.8 6.0 12.0 風(fēng)險(xiǎn)最低的股票是( ),。
- 單選題 公司賣(mài)出了一個(gè)看跌期權(quán),行權(quán)價(jià)格為$56,,同時(shí)購(gòu)買(mǎi)了一個(gè)行權(quán)價(jià)格為$44的看漲期權(quán),;購(gòu)買(mǎi)期權(quán)時(shí)股票的價(jià)格為$44;看漲期權(quán)費(fèi)為$5,看跌期權(quán)費(fèi)為$4,,目前的價(jià)格上漲了$7,,那么ABC公司因?yàn)榭礉q期權(quán)取得或是損失的金額為多少( )。








 津公網(wǎng)安備12010202000755號(hào)
津公網(wǎng)安備12010202000755號(hào)