? 6.1 Credit rating
Standard & Poor’s | Definition |
AAA, AA+, AAA-, AA-, A+ | Excellent quality, lowest default risk |
A, A-, BBB+ | Good quality, low default risk |
BBB, BBB-, BB+ | Medium rating |
BB or below | Junk bonds (speculative, high default risk) |
The extra return (or yield spread) required by investors on a bond will depend on its credit ratings and its maturity.
This is often quoted as an adjustments to the risk free rate in basis points. (1 point =0.01%)
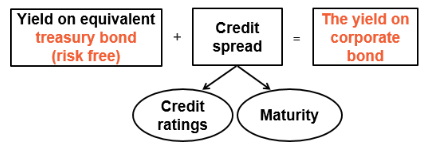
Cost of debt = (risk free rate + credit spread)×(1- tax rate)
##knowlegePointIds:( Credit rating)##
##end##
##start00:03:09##
? 6.2 Yield curve
The yield curve shows how the yield on government bonds vary according to the term of the borrowing.
The curve shows the yield expected by the investors assuming that the bond pays all of the return as a single payment on maturity.
Normally it is upward sloping.
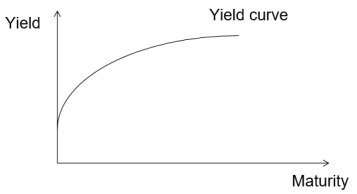
There are a number of explanations of the yield curve; at any one time both may be influencing the shape of the yield curve.
a. Expectations theory
b. Liquidity preference theory
a. Expectations theory – the curve reflects expectations that interest rates will rise in the future, so the government has to offer higher returns on long-term debt.
b. Liquidity preference theory – the curve reflects the compensation that investors require higher annual returns for sacrificing liquidity on long-dated bonds.