Threats and safeguards for accountants
(會(huì)計(jì)師所面臨的威脅以及如何防范)
4. Threats and safeguards for accountants
Threats to independence of action and conflicts of interest include:
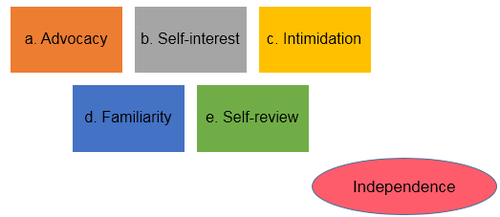
4.1 Advocacy threat
An advocacy threat arises in certain situations where the audit firm assumes the client's part in a dispute or somehow acts as their advocate. The most obvious instance of this would be when a firm acts as an expert witness in a court case in support of its audit client.
Relevant safeguards might be:
a. Using different departments in the firm to carry out the work
b. Making full disclosure to the client's audit committee
c. Withdrawal from an engagement if the risk to independence is considered too great
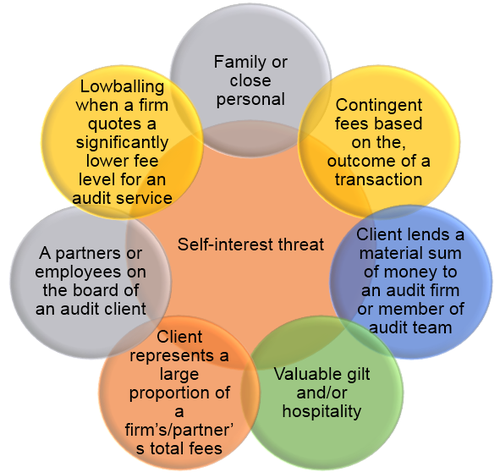
4.2 Self-interest threat
The ACCA Code of Ethics and Conduct (2011) highlights a great number of areas in which a self-interest threat to independence might arise (frequently in the context of the external auditor, but generally applicable to all members)
Example
4.3 Self-interest threat
Safeguards in these situations might include:
a. Discussing the issues with the audit committee of the client
b. Taking steps to reduce the dependency on the client
c. Consulting an independent third party such as ACCA
d. Maintaining records such that the firm is able to demonstrate that appropriate staff and time are spent on the engagement
e. Compliance with all applicable audit standards, guidelines and quality control procedures
Intimidation threat
An intimidation threat arises when a professional accountant is deterred from acting objectively by threats, actual or perceived. Situations which might create intimidation threats include:
a. Threats of dismissal
b. Threats of litigation
c. Pressure to reduce fees or the extent of work performed
Safeguards would include disclosure of such threats to the audit committee for their consideration, review of work for any evidence of bias and even the possibility of removing affected individuals from the area under threat.
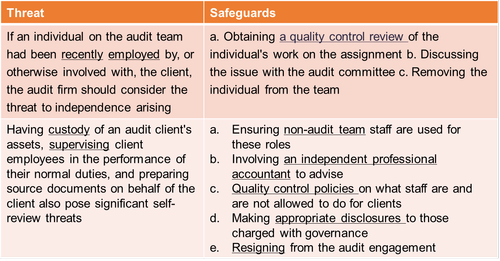
4.4 Familiarity threat
Familiarity threat is where independence is jeopardized by the audit firm and its staff becoming over-familiar with the client and its staff. As a result they may become too sympathetic to their views and interests.
Safeguards usually include rotation of affected individuals away from the position creating the threat and a quality control review of anyone's work if there is a familiarity threat present.
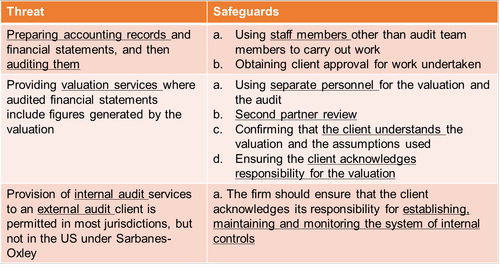
4.5 Self-review threat
Self-review threat is where an audit firm provides services other than audit services to an audit client (ie providing multiple services).
Example